Lafayette
Yes
No
No
Fish and Aquatic Life
Overview
Steiner Branch is a Class II and Class III trout stream (WDNR, 1980) tributary to the Yellowstone River at Lake Yellowstone. It had suffered from extreme sedimentation due to agricultural land use practices in the early 1980s (WDNR, 19931). These practices have been altered or eliminated, primarily because of land acquisition for the Yellowstone Wildlife Area. A dam on the headwaters of the creek affects water quality and is probably preventing the creek from meeting its full cold water fishery potential (Van Dyck, 1994).
Date
Author Aquatic Biologist
Historical Description
Steiner Branch, T4N, R4E, Sections 34-5, Surface acres = 1.3, Miles = 2.3, Gradient = 74.0 feet per mile, Total alkalinity = 268 mg/l, Volume of flow = 1.0 cfs.
Although originating from warm water drainage, Steiner Branch soon receives much of its volume of flow from good springs near its headwaters. It is stocked annually with brown trout. Almost 100 percent of the land area within the watershed is used for agricultural purposes. Most of the immediate floodplain is meadow and firm pasture, while the higher land is cropped. Bank erosion ranges from light to moderate and gravel is the most common bottom type. About one-half mile of stream length is in the Yellowstone Lake Wildlife Area and includes its mouth which is located above Yellowstone Lake. Game species include deer, squirrel, ruffed grouse, Hungarian partridge and quail on the uplands and muskrats and some waterfowl on the stream itself. The stream is also accessible from two road crossings.
From: Piening, Ronald; Poff, Ronald; Threinen, C.W., 1967. Lake and Stream Classification Project. Surface Water Resources of Lafayette County, Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources, Madison, WI.
Date 1967
Author Surface Water Inventory Of Wisconsin
General Condition
Steiner Branch (904000), from the mouth to trib 904300, was assessed during the 2018 listing cycle; new biological (fish Index of Biotic Integrity (IBI) scores) and temperature sample data were clearly below the 2018 WisCALM listing thresholds for the Fish and Aquatic Life use. This water was meeting this designated use and was not considered impaired.
Date 2017
Author Ashley Beranek
Condition
Wisconsin has over 84,000 miles of streams, 15,000 lakes and milllions of acres of wetlands. Assessing the condition of this vast amount of water is challenging. The state's water monitoring program uses a media-based, cross-program approach to analyze water condition. An updated monitoring strategy (2015-2020) is now available. Compliance with Clean Water Act fishable, swimmable standards are located in the Executive Summary of Water Condition in 2018. See also the 'monitoring and projects' tab.
Reports
Management Goals
Wisconsin's Water Quality Standards provide qualitative and quantitative goals for waters that are protective of Fishable, Swimmable conditions [Learn more]. Waters that do not meet water quality standards are considered impaired and restoration actions are planned and carried out until the water is once again fishable and swimmable
Management goals can include creation or implementation of a Total Maximum Daily Load analysis, a Nine Key Element Plan, or other restoration work, education and outreach and more. If specific recommendations exist for this water, they will be displayed below online.
Monitoring
Monitoring the condition of a river, stream, or lake includes gathering physical, chemical, biological, and habitat data. Comprehensive studies often gather all these parameters in great detail, while lighter assessment events will involve sampling physical, chemical and biological data such as macroinvertebrates. Aquatic macroinvertebrates and fish communities integrate watershed or catchment condition, providing great insight into overall ecosystem health. Chemical and habitat parameters tell researchers more about human induced problems including contaminated runoff, point source dischargers, or habitat issues that foster or limit the potential of aquatic communities to thrive in a given area. Wisconsin's Water Monitoring Strategy was recenty updated.
Grants and Management Projects
Monitoring Projects
| WBIC | Official Waterbody Name | Station ID | Station Name | Earliest Fieldwork Date | Latest Fieldwork Date | View Station | View Data |
|---|
| 904000 | Steiner Br | 10008010 | Steiner Br. Station 3 | 11/15/2000 | 11/15/2000 | Map | Data |
| 904000 | Steiner Br | 10022553 | Steiner Branch Baseline Upper | 1/1/2015 | 10/14/2016 | Map | Data |
|
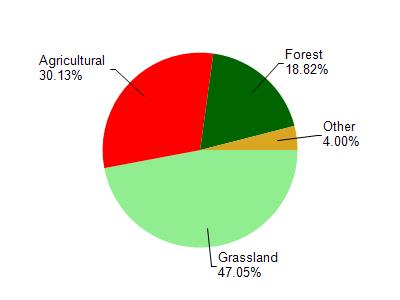
Watershed Characteristics
Steiner Br is located in the Yellowstone River watershed which is 57.46 mi². Land use in the watershed is primarily grassland (47%), agricultural (30.10%) and a mix of forest (18.80%) and other uses (4.00%). This watershed has 158.93 stream miles, 9.53 lake acres and 636.16 wetland acres.
Nonpoint Source Characteristics
This watershed is ranked High for runoff impacts on streams, Medium for runoff impacts on lakes and High for runoff impacts on groundwater and therefore has an overall rank of High. This value can be used in ranking the watershed or individual waterbodies for grant funding under state and county programs.However, all waters are affected by diffuse pollutant sources regardless of initial water quality. Applications for specific runoff projects under state or county grant programs may be pursued. For more information, go to surface water program grants.