Trempealeau
No
No
No
Fish and Aquatic Life
Overview
Bugle Lake is a 35 acre impoundment of Elk Creek in the City of Independence. Bugle Lake has a maximum depth of eight feet and a mean depth of 5.8 feet, based on measurements in its lower 21 acres. The contributing watershed area is approximately 112 square miles (71,849 acres). Both upland and stream bank erosion are significant problems in the Elk Creek watershed. Because of extensive erosion within the watershed, Bugle Lake has a long history of sedimentation problems, dating back to its creation in 1877.
Date 1996
Author Aquatic Biologist
Historical Description
Source: 1970, Surface Water Resources of Trempealeau County Bugle Lake, T22N, R9W, S25 Surface Acres = 34.7, S.D.F. = 2.78, Maximum Depth = 10 feet.
A medium hard water, drainage impoundment located on Elk Creed within the City of Independence. Its maximum depth is controlled by stoplogs and a tainter gate. The dam is owned by the city and it has a height of 10 feet. The water is clear, alkaline, and has a low transparency. Largemouth bass and bluegill comprise the major fishery and were stocked following chemical treatment in 1966 to remove carp, suckers, and small forage fish species. Some brown and rainbow trout are present. Carp are again present, but were not a problem at this writing. There is public access from two parks. Migrant puddle ducks use the impoundment.
Date 1970
Author Surface Water Inventory Of Wisconsin
General Condition
A self-help volunteer and Adopt-A-Lake participants on this lake could aid in documenting water quality trends and in increasing awareness about and protective actions for this lake. WDNR Watershed Management staff could collect other water quality data to build on past collection efforts.
Restoration Efforts
In 1979, the Elk Creek watershed was selected as a WDNR Nonpoint Source Priority Watershed Program and best management practices (BMPs) were implemented from 1980 to 1988. Watershed improvements due to these BMPs included upland erosion control practices, stream bank stabilization and fencing, and barnyard runoff controls. During this same period, frequent complaints of shallowness and turbidity in Bugle Lake led to a lake rehabilitation feasibility study. WDNR accepted a proposed dredging project for Bugle Lake under its Office of Inland Lakes Renewal (OILR).
Hydraulic dredging on Bugle Lake during 1981 removed about 175,000 cubic yards of sediment from 21.5 acres, based on lake volume estimates. The total project cost, including dredge spoil site preparation, dredging, engineering, administration, and watershed improvements - primarily stream bank riprapping - was $505,680 (Marshall). The millpond was dredged to a uniform depth of 10 feet with moderately sloped sides. As a result, the lake's volume almost tripled from 61 acre ft. to about 170 acre ft (Table 29).
The Bugle Lake Protection and Rehabilitation Project Final Report (1982) estimated the sediment delivery rate to the lake could be reduced 50 60 percent, to about 19,800 cubic yards per year, by implementing watershed improvements. The report projected that the lake's life expectancy would be 25 30 years following dredging.
Results
Unfortunately, watershed improvements did not meet earlier expectations. Stream bank erosion continues to be a serious problem. Despite efforts of the priority watershed project, approximately 60 percent of identified eroding stream banks in the watershed were not controlled. (Schreiber).
Estimates from field survey data in 1983 and 1989 indicate a higher sedimentation rate and more rapid decline in lake volume than anticipated: See "Bugle Lake Sedimentation Rates Since 1981" (Table 29), "Bugle Lake Bathymetry" (Figure 3), and "Changes in Volume of Bugle Lake".
By January 1989, lake volume had already declined 30 percent in the dredged area, decreasing from 170 acre ft. to 119 acre ft. During these eight years, approximately 82,600 cubic yards of sediment were deposited in the lake. This amounts to an average sedimentation rate of 10,325 cubic yards per year, or 3.6 inches per year.
Assuming an average trap efficiency of 33 percent (Brune), the estimated average sediment delivery rate to Bugle Lake from 1981 to 1989 was 31,288 cubic yards per year. This is a 58 percent higher sediment delivery rate than the 19,800 yards per year hoped for in the 1982 Project Final Report.
A somewhat different estimate was made in a 1980 USGS study of the Elk Creek Watershed. USGS estimated the sediment delivery rate to be about 24,790 cubic yards per year. However, this estimate could be higher than normal due to a 28 percent above-normal stream flow for 1980. Using the 1980 USGS estimated sediment delivery rate (24,790 cubic yards per year) and the average inflow rate of 67.4 cubic feet per second (cfs), which was adjusted down 28 percent from 1980 stream flow level, life expectancy for the millpond was estimated using the Brune curve to estimate trapping efficiency with declining lake volume. Trap efficiency values were obtained from the high curve for sediment trapping efficiency because of the perceived coarse nature of transported sediments.
Based on the above assumptions, it would take approximately 21 years, rather than the 25 30 years originally estimated, for Bugle Lake to return to its pre dredged volume. This means that by the year 2002, the City of Independence will once again have to address sedimentation in Bugle Lake.
Sedimentation in the lake varied substantially with time and location. For example, average sediment deposition of 6.5 inches for the entire lake was much higher during the first 22 months compared to the average 2.8 inches for the last six years. With respect to location, a comparison of average sedimentation in the lower versus upper end of the lake indicated as much as 3.5 times more deposition in the upper end.
A noticeable delta has developed in the northwest portion of the lake where Elk Creek enters the impoundment. Sediment deposition in the delta has been extremely high, as much as one foot per year. In the lower end, deposition has been much less, roughly 2 inches per year.
Conclusions
Many factors could explain why Bugle Lake is filling in more quickly than expected. One reason may be the continued contributions from upstream erosion. As cited previously, 60 percent of the identified eroding stream banks were not controlled by the priority watershed project. Another reason may be that watershed improvements implemented over the last nine years would have little effect on the movement of existing channel sediments, also known as bedload. After the lake was dredged, high levels of sediment delivery to the lake could have resulted from channel scouring, or head cutting, immediately above the lake. The large discrepancy between sedimentation in the upper and lower ends, plus the high deposition rate immediately following dredging, suggest that channel scouring of relatively coarse bedload material is a major contributor to sedimentation in Bugle Lake.
In its present state, Bugle Lake supports a marginal bass and walleye fishery with some natural reproduction. Trout species have also been stocked in the lake and in Elk Creek. Dredging the lake to a uniform depth provided poor game fish habitat. Thus, fish cribs have been placed in the lake to provide some structure. An annual ice fishing contest sponsored by the Elk Rod and Gun Club has become an important community event and fundraiser. Despite the rehabilitation project, the quality of the fishery is expected to decline as sedimentation progresses (Talley).
Date 1996
Author Aquatic Biologist
Impaired Waters
Island Park Beach on Bugle Lake was evaluated for bacteria in the 2022 cycle; E. coli levels were above listing thresholds as outlined in 2022 WisCALM. This beach was added to the 2022 Impaired Waters List.
Date 2022
Author Ashley Beranek
Condition
Wisconsin has over 84,000 miles of streams, 15,000 lakes and milllions of acres of wetlands. Assessing the condition of this vast amount of water is challenging. The state's water monitoring program uses a media-based, cross-program approach to analyze water condition. An updated monitoring strategy (2015-2020) is now available. Compliance with Clean Water Act fishable, swimmable standards are located in the Executive Summary of Water Condition in 2018. See also the 'monitoring and projects' tab.
Reports
Management Goals
Wisconsin's Water Quality Standards provide qualitative and quantitative goals for waters that are protective of Fishable, Swimmable conditions [Learn more]. Waters that do not meet water quality standards are considered impaired and restoration actions are planned and carried out until the water is once again fishable and swimmable
Management goals can include creation or implementation of a Total Maximum Daily Load analysis, a Nine Key Element Plan, or other restoration work, education and outreach and more. If specific recommendations exist for this water, they will be displayed below online.
Monitoring
Monitoring the condition of a river, stream, or lake includes gathering physical, chemical, biological, and habitat data. Comprehensive studies often gather all these parameters in great detail, while lighter assessment events will involve sampling physical, chemical and biological data such as macroinvertebrates. Aquatic macroinvertebrates and fish communities integrate watershed or catchment condition, providing great insight into overall ecosystem health. Chemical and habitat parameters tell researchers more about human induced problems including contaminated runoff, point source dischargers, or habitat issues that foster or limit the potential of aquatic communities to thrive in a given area. Wisconsin's Water Monitoring Strategy was recenty updated.
Grants and Management Projects
Monitoring Projects
| WBIC | Official Waterbody Name | Station ID | Station Name | Earliest Fieldwork Date | Latest Fieldwork Date | View Station | View Data |
|---|
| 1782700 | Bugle Lake | 623262 | Bugle Lake - Deep Hole | 8/1/1986 | 1/13/2000 | Map | Data |
| 1782700 | Bugle Lake | 10043924 | Island Park Beach, Bugle Lake | 6/21/2016 | 5/28/2025 | Map | Data |
| 1782700 | Bugle Lake | 10005933 | Bugle Lake - Highway 93 - 50 Feet Upstream Of Bridge Deepest Spot | 8/29/2000 | 9/15/2015 | Map | Data |
|
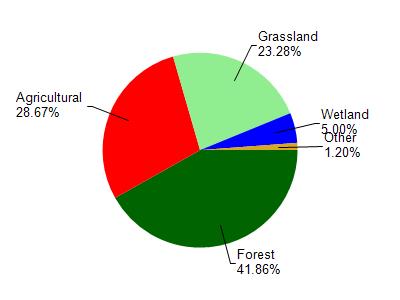
Watershed Characteristics
Bugle Lake is located in the Elk Creek watershed which is 112.95 mi². Land use in the watershed is primarily forest (41.90%), agricultural (28.70%) and a mix of grassland (23.30%) and other uses (6.20%). This watershed has 284.80 stream miles, 47.13 lake acres and 3,310.85 wetland acres.
Nonpoint Source Characteristics
This watershed is ranked Not Available for runoff impacts on streams, Not Available for runoff impacts on lakes and High for runoff impacts on groundwater and therefore has an overall rank of High. This value can be used in ranking the watershed or individual waterbodies for grant funding under state and county programs.However, all waters are affected by diffuse pollutant sources regardless of initial water quality. Applications for specific runoff projects under state or county grant programs may be pursued. For more information, go to surface water program grants.