Iron
No
No
No
Fish and Aquatic Life
Overview
The Montreal River forms part of the Michigan-Wisconsin border. The West Fork flows from Island Lake, through the Gile Flowage (pronounced Aguile@) and paralleling the East Fork for many miles before meeting. The East Fork of the Montreal River originates at Pine Lake, eventually forming the border between Ironwood and Hurley before becoming the Montreal River at the junction with the West Fork. All three reaches of the river include trout waters.
Muskrat, mink and beaver occur upstream from Hurley. Stream flow is variable, with gradient increasing downstream of Hurley. The cities of Hurley, WI and Ironwood, MI, discharge into this sub-watershed. The West Fork of the Montreal River above Gile Flowage is considered a warm water fishery including young walleye, perch, crappies, northern pike and the occasional brook trout. Downstream from the Gile Flowage, walleye, muskellunge and some brook trout occur. Beaver and nesting and migratory waterfowl use the upper watershed. The Montreal River West Fork receives the effluent discharge from the city of Montreal. The Montreal River is considered trout water to its mouth.
The mouth of the Montreal River has been identified by the Lake Superior Binational Program as important to the integrity of the Lake Superior ecosystem for old growth forest, coastal wetlands and fish and wildlife spawning and nursery grounds. Privately held land at the mouth of the river forms a four-acre cove with a 25-foot-deep kettle hole. Wetlands in the area are valuable to plants and animals. In June and July, the area is used by spawning white suckers and sturgeon and emerald and spottail shiners. The mouth and lower river are also used by spawning coho salmon, pink salmon and rainbow trout. Above the Superior Falls dam, the Montreal River is a high-quality trout stream that requires some additional stocking to ensure a balanced fishery. A scenic area exists below Superior Falls where 100-year-old cedars line the banks. Migratory fish move about a third of a mile upstream to Superior Falls.
The West Fork Montreal River is identified in the Coastal Wetlands Evaluation (Epstein 1997) as an aquatic priority site. While only 17 taxa were collected in this initial effort, two of these are very rare in Wisconsin. The predominant groups were mayflies and caddisflies. Turbidity and impoundment present challenges to the maintenance of water quality.
From: Turville-Heitz, Meg. 1999. Lake Superior Basin Water Quality Management Plan. Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources, Madison, WI.
Date 1999
Author Aquatic Biologist
Overview
The Gile Flowage on the West Fork Montreal River is a headwater storage reservoir essential to the operation of the two hydropower projects downstream on the Montreal River. Northern States Power draws and refills the Gile Flowage to provide seasonally uniform streamflow for maximum generation at its Superior Falls and Saxon Falls hydro projects. The flowage is gradually lowered in winter in anticipation of collecting and storing spring runoff. That stored water is then gradually released to maintain flows during summer.
WDNR asked the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) to analyze the effects of winter drawdowns as part of the cumulative impacts analysis for the Superior Falls Hydro licensing decision. FERC denied the request, citing that it had no authority at the Gile Flowage. FERC subsequently initiated an investigation of its jurisdiction at the Gile Flowage, but has yet to make a decision on its authority. WDNR suggested a moderation of the drawdown over a three-year test period to see if there is any change in walleye fingerling survival. If no evidence came from the study showing that modified drawdown altered walleye survivability, the traditional operating procedures could resume. Northern States Power declined to participate in the study, citing economic concerns, regulatory uncertainties and increased liabilities as a result of flooding, and has suggested the fingerling survival might be related to other factors such as entrainment in the works of the dam.
The Saxon Falls Hydro project, relicensed in 1989, was one of the first projects in Wisconsin to be relicensed after Congress passed the Electric Consumers' Protection Act in 1986. With this amendment to the Federal Power Act, FERC is required to give equal consideration to both power generation and environmental protection in deciding whether or not to issue a project license. Michigan Department of Natural Resources participated in the licensing consultation for the Saxon Project. One of the resource issues at Saxon Falls was a minimum flow requirement to the bypassed reach of the Montreal River. WDNR and Northern States Power conducted a qualitative flow study to determine what level of discharge would maintain aquatic and aesthetic resources in the dewatered segment where flow was diverted to the powerhouse. FERC ordered Northern States Power to continuously release at least 5 cubic feet per second to the bypassed channel. The license order for Saxon Falls Project is final, with a term of 30 years. No party requested a rehearing on FERC's order when it was issued in 1989.
From: Turville-Heitz, Meg. 1999. Lake Superior Basin Water Quality Management Plan. Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources, Madison, WI.
Date 1999
Author Aquatic Biologist
Overview
For the Superior Falls Hydro project, both WDNR and Michigan DNR participated in the consultation on the license application. Since the discharge at the powerhouse is located on the Michigan side of the river, Michigan has the responsibility for issuing, waiving or denying water quality certification under Section 401 of the Clean Water Act. Because Michigan DNR did not act on Northern States Power's request for water quality certification within the one year allotted to respond, FERC presumed that the need for certification was waived.
The project occupies the site of a natural waterfall just upstream from the Montreal River's mouth. Therefore, WDNR determined that fish passage around the dam and losses from fish entrainment in the works of the dam were not a significant concern at the Superior Falls project. Michigan DNR, however, requested Northern States Power provide a barrier to prevent fish entrainment and compensate for residual losses that occur after installation. Michigan DNR requested a specific reopener clause in the license that would trigger a FERC review of fish passage.
In the new license for the Superior Falls Project, FERC ordered the operator to provide a minimum flow of 20 cfs during daytime viewing hours, and a minimum of 8 cfs in the night time hours during the summer season for aesthetics in the bypassed reach. Maintenance of stable water levels in the impoundment and stable discharge from the dam is also an important resource concern at this project due to the flashiness of the river, the small storage capacity of the reservoir and the equipment and staff limitations. FERC ordered the project be run in a run-of-river mode, with exceptions for extreme conditions outside of the licensee's control. Both Northern States Power and Michigan DNR requested rehearing of the FERC license order. WDNR did not request a rehearing.
From: Turville-Heitz, Meg. 1999. Lake Superior Basin Water Quality Management Plan. Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources, Madison, WI.
Date 1999
Author Aquatic Biologist
Management Goals
Wisconsin's Water Quality Standards provide qualitative and quantitative goals for waters that are protective of Fishable, Swimmable conditions [Learn more]. Waters that do not meet water quality standards are considered impaired and restoration actions are planned and carried out until the water is once again fishable and swimmable
Management goals can include creation or implementation of a Total Maximum Daily Load analysis, a Nine Key Element Plan, or other restoration work, education and outreach and more. If specific recommendations exist for this water, they will be displayed below online.
Monitoring
Monitoring the condition of a river, stream, or lake includes gathering physical, chemical, biological, and habitat data. Comprehensive studies often gather all these parameters in great detail, while lighter assessment events will involve sampling physical, chemical and biological data such as macroinvertebrates. Aquatic macroinvertebrates and fish communities integrate watershed or catchment condition, providing great insight into overall ecosystem health. Chemical and habitat parameters tell researchers more about human induced problems including contaminated runoff, point source dischargers, or habitat issues that foster or limit the potential of aquatic communities to thrive in a given area. Wisconsin's Water Monitoring Strategy was recenty updated.
Grants and Management Projects
Monitoring Projects
| WBIC | Official Waterbody Name | Station ID | Station Name | Earliest Fieldwork Date | Latest Fieldwork Date | View Station | View Data |
|---|
| 2940300 | Montreal River | 10031229 | Montreal River below Superior Falls Flowage | 4/26/2010 | 1/1/2015 | Map | Data |
| 2940600 | Superior Falls Flowage | 10022264 | Superior Falls Flowage WI-MI | 6/29/2010 | 8/30/2012 | Map | Data |
| 2940300 | Montreal River | 263001 | Montreal River - Hwy 122 | 9/1/1988 | 1/1/2015 | Map | Data |
| 2940600 | Superior Falls Flowage | 10043310 | Montreal River below Saxon Falls Dam | | | Map | Data |
| 2940300 | Montreal River | 10043317 | Montreal River Below Saxon Falls | | | Map | Data |
| 2940600 | Superior Falls Flowage | 10043317 | Montreal River Below Saxon Falls | | | Map | Data |
| 2940600 | Superior Falls Flowage | 10031229 | Montreal River below Superior Falls Flowage | 4/26/2010 | 1/1/2015 | Map | Data |
| 2940300 | Montreal River | 10043310 | Montreal River below Saxon Falls Dam | | | Map | Data |
|
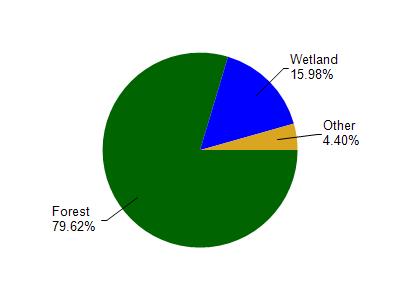
Watershed Characteristics
Montreal River is located in the Potato River watershed which is 139.92 mi². Land use in the watershed is primarily forest (79.70%), wetland (16%) and a mix of grassland (2.40%) and other uses (2.00%). This watershed has 306.29 stream miles, 195.98 lake acres and 14,309.56 wetland acres.
Nonpoint Source Characteristics
This watershed is ranked Not Ranked for runoff impacts on streams, Not Available for runoff impacts on lakes and Low for runoff impacts on groundwater and therefore has an overall rank of Low. This value can be used in ranking the watershed or individual waterbodies for grant funding under state and county programs.However, all waters are affected by diffuse pollutant sources regardless of initial water quality. Applications for specific runoff projects under state or county grant programs may be pursued. For more information, go to surface water program grants.