
2.63 Miles
0 - 2.63
Cool-Cold Headwater, Cool-Warm Headwater
2025
Poor
Acute Aquatic Toxicity, Degraded Biological Community, Low DO, Degraded Habitat, Chronic Aquatic Toxicity
Unspecified Metals, Chloride, Total Phosphorus, Sediment/Total Suspended Solids
Milwaukee
No
No
Yes
Fish and Aquatic Life
Overview
Indian Creek, in the Milwaukee River South Watershed, is a 2.63 mile river that falls in Milwaukee County. This river is managed for fishing and swimming and is currently considered impaired.
Date 2011
Author Aquatic Biologist
Impaired Waters
Indian Creek was put on the Impaired Waters List in the 1998 cycle for unspecified metals causing aquatic toxicity, phosphorus causing low DO and degraded biology, and sediment causing degraded habitat and elevated temperature. Indian Creek was evaluated every two-year cycle from 2014 to 2022. The phosphorus impairment was confirmed in all cycles. A chloride impairment was found in the 2018 cycle and confirmed in the 2020 cycle. In the 2022 cycle temperature evaluation showed the impairment of elevated temperature could be removed. The phosphorus and sediment listings are covered by the Milwaukee River TMDL, approved in 2018.
Date 2022
Author Ashley Beranek
Condition
Wisconsin has over 84,000 miles of streams, 15,000 lakes and milllions of acres of wetlands. Assessing the condition of this vast amount of water is challenging. The state's water monitoring program uses a media-based, cross-program approach to analyze water condition. An updated monitoring strategy (2015-2020) is now available. Compliance with Clean Water Act fishable, swimmable standards are located in the Executive Summary of Water Condition in 2018. See also the 'monitoring and projects' tab.
Reports
Recommendations
Citizen-Based Stream Monitoring
Collect chemical, physical, and/or biological water quality data to assess the current overall stream health. The data can inform management decisions and may be used to identify impaired waters for biennial lists.
Management Goals
Wisconsin's Water Quality Standards provide qualitative and quantitative goals for waters that are protective of Fishable, Swimmable conditions [Learn more]. Waters that do not meet water quality standards are considered impaired and restoration actions are planned and carried out until the water is once again fishable and swimmable
Management goals can include creation or implementation of a Total Maximum Daily Load analysis, a Nine Key Element Plan, or other restoration work, education and outreach and more. If specific recommendations exist for this water, they will be displayed below online.
Monitoring
Monitoring the condition of a river, stream, or lake includes gathering physical, chemical, biological, and habitat data. Comprehensive studies often gather all these parameters in great detail, while lighter assessment events will involve sampling physical, chemical and biological data such as macroinvertebrates. Aquatic macroinvertebrates and fish communities integrate watershed or catchment condition, providing great insight into overall ecosystem health. Chemical and habitat parameters tell researchers more about human induced problems including contaminated runoff, point source dischargers, or habitat issues that foster or limit the potential of aquatic communities to thrive in a given area. Wisconsin's Water Monitoring Strategy was recenty updated.
Grants and Management Projects
Monitoring Projects
| WBIC | Official Waterbody Name | Station ID | Station Name | Earliest Fieldwork Date | Latest Fieldwork Date | View Station | View Data |
|---|
| 19600 | Indian Creek | 10047955 | Indian Creek US N Port Washington Road | 1/1/2015 | 1/1/2015 | Map | Data |
| 19600 | Indian Creek | 413664 | Indian Creek at Bradley Rd (Bi) | | | Map | Data |
| 19600 | Indian Creek | 10010587 | Indian Creek - 19 | 10/8/1997 | 10/8/1997 | Map | Data |
| 19600 | Indian Creek | 10047954 | Indian Creek DS N Manor Lane | 1/1/2015 | 1/1/2015 | Map | Data |
| 19600 | Indian Creek | 10022032 | Indian Creek | 10/30/2007 | 1/1/2015 | Map | Data |
| 19600 | Indian Creek | 10047773 | Indian Creek at E Dean Road | 1/1/2015 | 3/19/2017 | Map | Data |
| 19600 | Indian Creek | 10029949 | Indian Creek DS Bradley Road | 7/20/2008 | 11/12/2025 | Map | Data |
| 19600 | Indian Creek | 413065 | Indian Creek at Bradley Road | 5/28/1975 | 5/11/1992 | Map | Data |
|
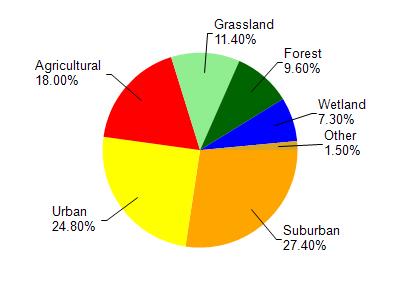
Watershed Characteristics
Indian Creek is located in the Milwaukee River South watershed which is 167.90 mi². Land use in the watershed is primarily suburban (27.40%), urban (24.80%) and a mix of agricultural (18%) and other uses (29.80%). This watershed has 203.63 stream miles, 13,038.94 lake acres and 5,996.03 wetland acres.
Nonpoint Source Characteristics
This watershed is ranked High for runoff impacts on streams, High for runoff impacts on lakes and High for runoff impacts on groundwater and therefore has an overall rank of High. This value can be used in ranking the watershed or individual waterbodies for grant funding under state and county programs.However, all waters are affected by diffuse pollutant sources regardless of initial water quality. Applications for specific runoff projects under state or county grant programs may be pursued. For more information, go to surface water program grants.
Indian Creek is considered a Cool-Cold Headwater, Cool-Warm Headwater under the state's Natural Community Determinations.
Natural communities (stream and lake natural communities) represent model results and DNR staff valiation processes that confirm or update predicted conditions based on flow and temperature modeling from historic and current landscape features and related variables. Predicated flow and temperatures for waters are associated predicated fish assemblages (communities). Biologists evaluate the model results against current survey data to determine if the modeled results are corect and whether biological indicators show water quaity degradation. This analysis is a core component of the state's resource management framework. Wisconsin's Riverine Natural Communities.
Cool (Warm-Transition) Headwaters are small, sometimes intermittent streams with cool to warm summer temperatures. Coldwater fishes are uncommon to absent, transitional fishes are abundant to common, and warm water fishes are common to uncommon. Headwater species are abundant to common, mainstem species are common to absent, and river species are absent.
Cool (Cold-Transition) Headwaters are small, usually perennial streams with cold to cool summer temperatures. Coldwater fishes are common to uncommon (<10 per 100 m), transitional fishes are abundant to common, and warm water fishes are uncommon to absent. Headwater species are abundant to common, mainstem species are common to absent, and river species are absent.