Details
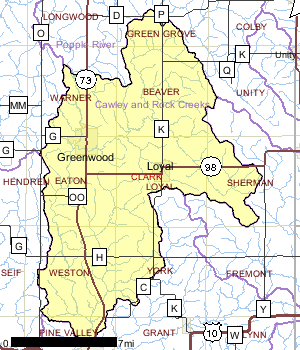
The Crawley and Rock Creeks Watershed is approximately 108,028 acres in size and consists of 343 miles of streams and rivers, 109 acres of lakes, and 6,082 acres of wetlands. The watershed is dominated by agriculture and forest but is ranked high for nonpoint source issues affecting groundwater in the watershed.
Date 1999
Nonpoint and Point Sources
Municipal and industrial point source discharges have historically degraded water quality in the streams of this watershed. Wastewater treatment plant upgrades and relocation of discharges have improved water quality in some of the degraded streams. Nonpoint sources of pollution are known to impact Cawley Creek, however direct knowledge of impacts to other streams is unknown at this time. Because of the high percentage of land in cultivation, the likelihood is quite high that nonpoint source impacts are affecting many streams in this watershed. What exacerbates water quality problems is the minimal groundwater recharge to streams which results in low base flows during prolonged dry periods. Additionally, precipitation and snowmelt rapidly increase stream flows in this watershed, which can also cause water quality problems.
Date 1999
Ecological Landscapes
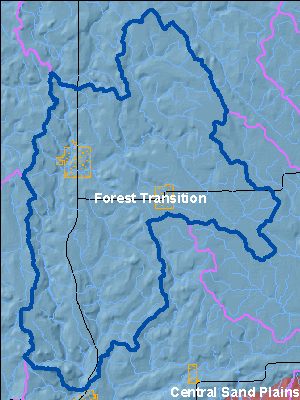
The Forest Transition Ecological Landscape lies along the northern border of Wisconsin's Tension Zone, through the central and western part of the state, and supports both northern forests and agricultural areas. The central portion of the Forest Transition lies primarily on a glacial till plain deposited by glaciation between 25,000 and 790,000 years ago. The eastern and western portions are on moraines of the Wisconsin glaciation. The growing season in this part of the state is long enough that agriculture is viable, although climatic conditions are not as favorable as in southern Wisconsin. Soils are diverse, ranging from sandy loam to loam or shallow silt loam, and from poorly drained to well drained.
The historic vegetation of the Forest Transition was primarily northern hardwood forest. These northern hardwoods were dominated by sugar maple and hemlock, and contained some yellow birch, red pine and white pine. Currently, over 60% of this Ecological Landscape is non-forested. Forested areas consist primarily of northern hardwoods and aspen, with smaller amounts of oak and lowland hardwoods. The eastern portion of the Ecological Landscape differs from the rest of the area in that it remains primarily forested, and includes some ecologically significant areas. Throughout the Ecological Landscape, small areas of conifer swamp are found near the headwaters of streams, and associated with lakes in kettle depressions on moraines. Ground flora show characteristics of both northern and southern Wisconsin, as this Ecological Landscape lies along the Tension Zone.
Date 2010
Hydrologic Features
Water quality problems are exacerbated by the minimal groundwater recharge to streams which results in low base flows during prolonged dry periods. Additionally, precipitation and snowmelt rapidly increase stream flows in this watershed, which can also cause water quality problems.
Date 1999
Fisheries
Cawley Creek is a stream located just 2.3 miles from Neillsville, in the state of Wisconsin, United States. Fishermen will find a variety of fish including rainbow trout, brown trout and channel catfish here. Whether youre fly fishing, spinning or baitcasting your chances of getting a bite here are good.
Cawley Creek is a stream located just 2.3 miles from Neillsville, in the state of Wisconsin, United States. Fishermen will find a variety of fish including rainbow trout, brown trout and channel catfish here.
Date 2011
Wildlife and Habitat
Two aquatic dependent species of concern have been documented in this watershed. Management decisions should consider potential affects to these species. Other species may be present but not yet documented.
Date 1999
Watershed RecommendationsCitizen Stream Monitoring
Date
Status
Collect chemical, physical, and/or biological water quality data to assess the current overall stream health. The data can inform management decisions and may be used to identify impaired waters for biennial lists.
1/1/2012
In Progress
Citizen Stream Monitoring
Date
Status
Collect chemical, physical, and/or biological water quality data to assess the current overall stream health. The data can inform management decisions and may be used to identify impaired waters for biennial lists.
1/1/2012
In Progress
Citizen Stream Monitoring
Date
Status
Collect chemical, physical, and/or biological water quality data to assess the current overall stream health. The data can inform management decisions and may be used to identify impaired waters for biennial lists.
1/1/2012
In Progress
Monitor biology on WBIC: 1750400
Date
Status
Conduct biological (mIBI or fIBI) monitoring on Unnamed, WBIC: 1750400, AU:5535060
5/21/2016
Proposed
Monitor biology on WBIC: 1751400
Date
Status
Conduct biological (mIBI or fIBI) monitoring on Nelson Creek, WBIC: 1751400, AU:14273
5/21/2016
Proposed
Monitor biology on WBIC: 1751000
Date
Status
Conduct biological (mIBI or fIBI) monitoring on Bear Creek, WBIC: 1751000, AU:14271
5/21/2016
Proposed
Monitor biology on WBIC: 1752100
Date
Status
Conduct biological (mIBI or fIBI) monitoring on Unnamed, WBIC: 1752100, AU:5722468
5/21/2016
Proposed
Monitor biology on WBIC: 1750100
Date
Status
Conduct biological (mIBI or fIBI) monitoring on Cawley Creek, WBIC: 1750100, AU:14268
5/21/2016
Proposed
Confirm FCA: IW pre-2000 data
Date
Status
1676700 name Black R. (Below Medford) TMDL ID 582 Start Mile 132.67 End Mile 168.4
11/21/2011
Proposed
Date
Status
WDNR staff should continue to encourage communities to develop wellhead protection plans in the Watershed and the whole basin.
7/1/2010
Proposed
Mead Lake TMDL
Date
Status
TMDL Development for Mead Lake in Clark County, WI. Mead Lake is highly eutrophic and exhibits excessive concentrations of phosphorus and chlorophyll (a measure of algal densities) in its surface waters during the summer months (USACE 2005). Sediment and phosphorus enters the lake via the South Fork Eau Claire River, from nonpoint sources of pollution.
7/1/2007
In Progress
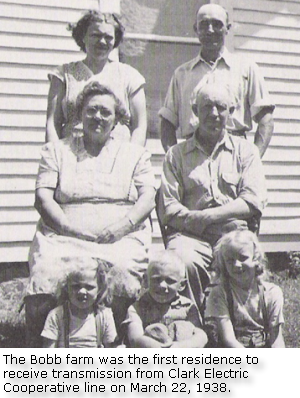 Watershed History Note
Watershed History NoteThe Cawley and Rock Creeks Watershed, located in Clark County, is home to the Clark Electric Cooperative. In the 1930's, 90% of the families living in rural areas had no access to electricity. The idea for an electric cooperative began in a county extension agent's office in Neillsville on March 24, 1937, where five men met to sign their names to an historic document - the Articles of Organization and Incorporation of the Clark Electric Cooperative. A brief history of the first 25 years of the cooperative follows.
The Ulen Construction Corporation of Lebanon, Indiana, received approval from the board of directors of Clark Electric Cooperative to construct 674 miles of distribution lines in numerous townships in the counties of Clark, Taylor and Marathon. The records show the first expenditure of co-op funds, as approved by the board of directors, were $25 for stationery and office forms, $12 for typewriter rental, $15 for adding machine rental, and $20 for office furniture rental.
During the board of directors meeting on July 15,1937, the problem of securing easements on property over which the lines would be built came up for discussion. C. F. Baldwin was hired to begin the easement job. He was to be paid 50¢ an hour and 5¢ per mile for the use of his car. Later, additional directors were added to the easement force. By the end of 1937 an office building was rented in Greenwood.
Membership applications rolled in during the early part of 1938. On March 22, 1938, the farm home of Mr. and Mrs. Arthur Bobb in the Thorp community was energized, the first on the lines of the Clark Electric Cooperative. By the end of April, more than 400 names were added to the cooperative's membership list. The members, for the most part, gave their cooperation to the easement solicitors, and by June 1938, total membership had reached 659. In 1941, the Clark Electric Cooperative connected the farm of Tom Jicinsky - the 2,000th farm to be connected. During the 1940's through the 1950's, the Clark Electric Cooperative sought various loans from the Rural Electric Administration (REA) for upgrades and improvements to its program.
Today in 2010, the Clark Electric Cooperative is alive and well and continues to meet the needs of its customers. Its website has information on compact florescent light bulbs, internet services and youth scholarships. For 73 years, its headquarters have remained in Greenwood, Wisconsin.
Photo at right is from http://wvls.lib.wi.us/ClarkCounty/clark/history/
Date 2010