Oneida
No
No
Yes
Fish and Aquatic Life
Overview
Big Lake, T38N, R11E, Section 21 Surface Acres = 865.8, S.D.F. = 1.72, Maximum Depth = 30 feet.
A soft water drainage lake having slightly alkaline, light brown water of low transparency. Sand is the chief littoral material (60 percent) with muck (23 percent) and some rock and gravel present. The shoreline is mostly upland (85 percent) with a limited wetland of coniferous-bog and shrub adjoining the lake. Muskellunge, northern pike, walleye, largemouth bass, smallmouth bass, perch, bluegill, crappie, rock bass, pumpkinseed, bullhead and sucker inhabit this lake. Public access without parking and navigable water access are available. Six resorts and 68 dwellings are found on the shoreline. As part of the three Lakes Chain, water levels are influenced by the dam on the Eagle River below Long Lake.
Date
Author Aquatic Biologist
Impaired Waters
Big Lake has a special fish consumption advisory for mercury in fish tissue. Big Lake was evaluated for phosphorus and algae every two years between 2014 and 2020. Phosphorus levels were consistently found to be too high, which was reflected in algal blooms.
Date 2019
Author Ashley Beranek
Impaired Waters
Big Lake (WBIC 1613000) was placed on the impaired waters list for Mercury in 1998 and for total phosphorus in 2014. The 2018 assessments showed continued impairment by phosphorus; total phosphorus sample data overwhelmingly exceeded 2018 WisCALM listing thresholds for the Recreation use and Fish and Aquatic Life use. Chlorophyll-a sample data exceeded the FAL use threshold, and were only nearly below the REC use thresholds. Based on the most updated information, no change in the existing impaired waters listing was needed.
Date 2017
Author Ashley Beranek
Impaired Waters
Big Lake (1613000) was placed on the impaired waters list for Mercury in 1998 and for total phosphorus in 2014. The 2016 assessments showed continued impairment by phosphorus; total phosphorus sample data overwhelmingly exceed 2016 WisCALM listing thresholds for the Recreation use and Fish and Aquatic Life use. Based on the most updated information, no change in existing impaired waters listing is needed.
Date 2015
Author Aaron Larson
Condition
Wisconsin has over 84,000 miles of streams, 15,000 lakes and milllions of acres of wetlands. Assessing the condition of this vast amount of water is challenging. The state's water monitoring program uses a media-based, cross-program approach to analyze water condition. An updated monitoring strategy (2015-2020) is now available. Compliance with Clean Water Act fishable, swimmable standards are located in the Executive Summary of Water Condition in 2018. See also the 'monitoring and projects' tab.
Reports
Recommendations
Management Goals
Wisconsin's Water Quality Standards provide qualitative and quantitative goals for waters that are protective of Fishable, Swimmable conditions [Learn more]. Waters that do not meet water quality standards are considered impaired and restoration actions are planned and carried out until the water is once again fishable and swimmable
Management goals can include creation or implementation of a Total Maximum Daily Load analysis, a Nine Key Element Plan, or other restoration work, education and outreach and more. If specific recommendations exist for this water, they will be displayed below online.
Monitoring
Monitoring the condition of a river, stream, or lake includes gathering physical, chemical, biological, and habitat data. Comprehensive studies often gather all these parameters in great detail, while lighter assessment events will involve sampling physical, chemical and biological data such as macroinvertebrates. Aquatic macroinvertebrates and fish communities integrate watershed or catchment condition, providing great insight into overall ecosystem health. Chemical and habitat parameters tell researchers more about human induced problems including contaminated runoff, point source dischargers, or habitat issues that foster or limit the potential of aquatic communities to thrive in a given area. Wisconsin's Water Monitoring Strategy was recenty updated.
Grants and Management Projects
Monitoring Projects
| WBIC | Official Waterbody Name | Station ID | Station Name | Earliest Fieldwork Date | Latest Fieldwork Date | View Station | View Data |
|---|
| 1613000 | Big Lake | 443055 | Big Lake - Deep Hole | 7/9/1979 | 8/17/2025 | Map | Data |
| 1613000 | Big Lake | 10004263 | Big Lake (3 Lakes Chain) | 7/27/1999 | 7/8/2022 | Map | Data |
| 1612900 | Dog Lake | 10004282 | Dog Lake | 7/27/1999 | 9/30/2017 | Map | Data |
| 1613000 | Big Lake | 10018959 | Big Lake -- Access Nr East Big Lake Loop Rd | 5/25/2007 | 6/25/2017 | Map | Data |
| 1613000 | Big Lake | 10019149 | Big Lake -- Access Nr Schultz Landing Loop Rd | 5/28/2006 | 7/4/2017 | Map | Data |
| 1613000 | Big Lake | 10042840 | Big Lake Eagle Lake Thoroughfare | 9/13/2014 | 9/13/2014 | Map | Data |
| 1599500 | Eagle River | 10004282 | Dog Lake | 7/27/1999 | 9/30/2017 | Map | Data |
| 1613000 | Big Lake | 443009 | Mocassin Lake - Lake Terrace Estates Stp | 7/30/1975 | 9/4/1985 | Map | Data |
| 1613000 | Big Lake | 10018960 | Big Lake Chain Of Lakes -- Access at NW Side Lake Nr Cw Smith Rd | 8/28/2002 | 8/17/2025 | Map | Data |
| 1599500 | Eagle River | 10004263 | Big Lake (3 Lakes Chain) | 7/27/1999 | 7/8/2022 | Map | Data |
|
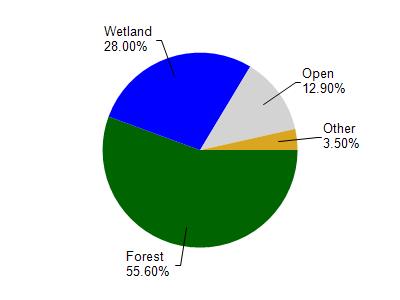
Watershed Characteristics
Big Lake is located in the Eagle River watershed which is 181.70 mi². Land use in the watershed is primarily forest (55.60%), wetland (28%) and a mix of open (12.90%) and other uses (3.50%). This watershed has 146.13 stream miles, 15,720.03 lake acres and 32,094.84 wetland acres.
Nonpoint Source Characteristics
This watershed is ranked Not Ranked for runoff impacts on streams, High for runoff impacts on lakes and Low for runoff impacts on groundwater and therefore has an overall rank of Low. This value can be used in ranking the watershed or individual waterbodies for grant funding under state and county programs.However, all waters are affected by diffuse pollutant sources regardless of initial water quality. Applications for specific runoff projects under state or county grant programs may be pursued. For more information, go to surface water program grants.